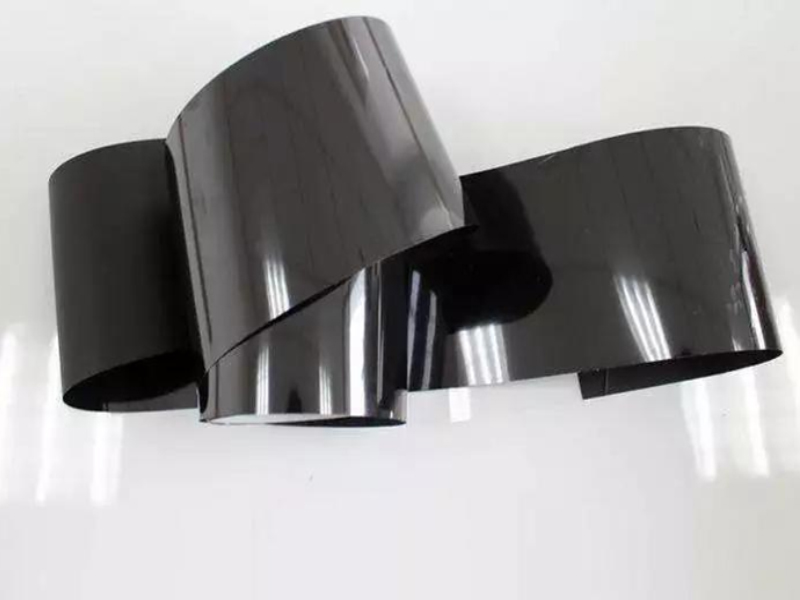
Thermal conductive graphite sheets are usually divided into graphene thermal conductive films and artificial graphite sheets.
Graphene thermal conductive film has a wide range of thermal conductivity, with a thermal conductivity of 600~1300W/m.k and a thickness of 0.05~0.3mm, providing customers with better choices; It has strong flexibility, low processing difficulty, and is not easily aged. It can adapt to the vast majority of chemical media. Due to its control of raw materials and production costs, graphene thermal conductive film is more cost-effective.
Artificial graphite sheets, made from polymer materials (polyimide) and sintered at 2800 ℃, have a thermal conductivity of up to 1700W/m.k; So the heat dissipation effect is better and faster. However, due to its better performance, the material cost is higher and the selling price is also higher. The smartphone industry is increasingly emphasizing quality, and the prospects for artificial graphite sheets are very optimistic.
Application scope of thermal conductive graphite sheets
Thermal conductive graphite sheets have excellent performance and can be combined with various materials to provide heat dissipation, such as metals, adhesives, plastics, and other materials. At the same time, it has low thermal resistance, light weight, and high thermal conductivity. In the 5G era, thermally conductive graphite sheets have been well developed, meeting the growing demand for industrial heat dissipation through thermal management solutions and providing new thermal management solutions for the electronics industry. With continuous technological innovation, thermally conductive graphite sheets will exhibit increasingly excellent thermal conductivity and develop a wider range of applications.
The processing process of thermally conductive graphite sheets
In order to meet the surface undulations of electronic devices and circuit modules, thermal conductive graphite sheets require certain processing to better adhere. Generally speaking, thermal conductive graphite sheets are processed with adhesive and film backing. Back adhesive treatment is used to better bond ICs and circuit boards, while back film processing is mainly applied in circuit designs that require insulation or heat insulation to maximize their functionality. Different products and materials use different processing methods.
Graphene thermal conductive film has a wide range of thermal conductivity, with a thermal conductivity of 600~1300W/m.k and a thickness of 0.05~0.3mm, providing customers with better choices; It has strong flexibility, low processing difficulty, and is not easily aged. It can adapt to the vast majority of chemical media. Due to its control of raw materials and production costs, graphene thermal conductive film is more cost-effective.
Artificial graphite sheets, made from polymer materials (polyimide) and sintered at 2800 ℃, have a thermal conductivity of up to 1700W/m.k; So the heat dissipation effect is better and faster. However, due to its better performance, the material cost is higher and the selling price is also higher. The smartphone industry is increasingly emphasizing quality, and the prospects for artificial graphite sheets are very optimistic.
Application scope of thermal conductive graphite sheets
Thermal conductive graphite sheets have excellent performance and can be combined with various materials to provide heat dissipation, such as metals, adhesives, plastics, and other materials. At the same time, it has low thermal resistance, light weight, and high thermal conductivity. In the 5G era, thermally conductive graphite sheets have been well developed, meeting the growing demand for industrial heat dissipation through thermal management solutions and providing new thermal management solutions for the electronics industry. With continuous technological innovation, thermally conductive graphite sheets will exhibit increasingly excellent thermal conductivity and develop a wider range of applications.
The processing process of thermally conductive graphite sheets
In order to meet the surface undulations of electronic devices and circuit modules, thermal conductive graphite sheets require certain processing to better adhere. Generally speaking, thermal conductive graphite sheets are processed with adhesive and film backing. Back adhesive treatment is used to better bond ICs and circuit boards, while back film processing is mainly applied in circuit designs that require insulation or heat insulation to maximize their functionality. Different products and materials use different processing methods.